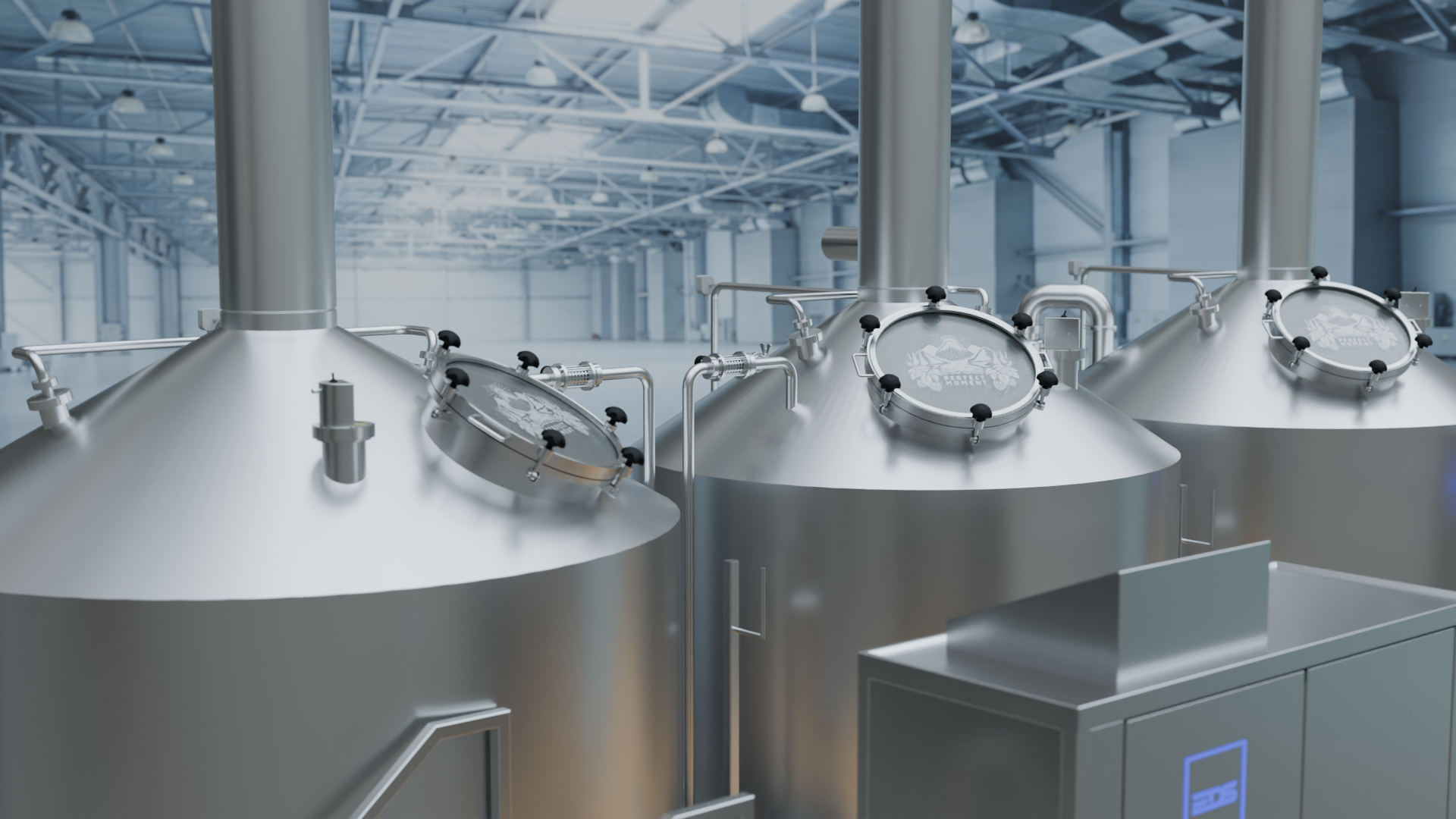
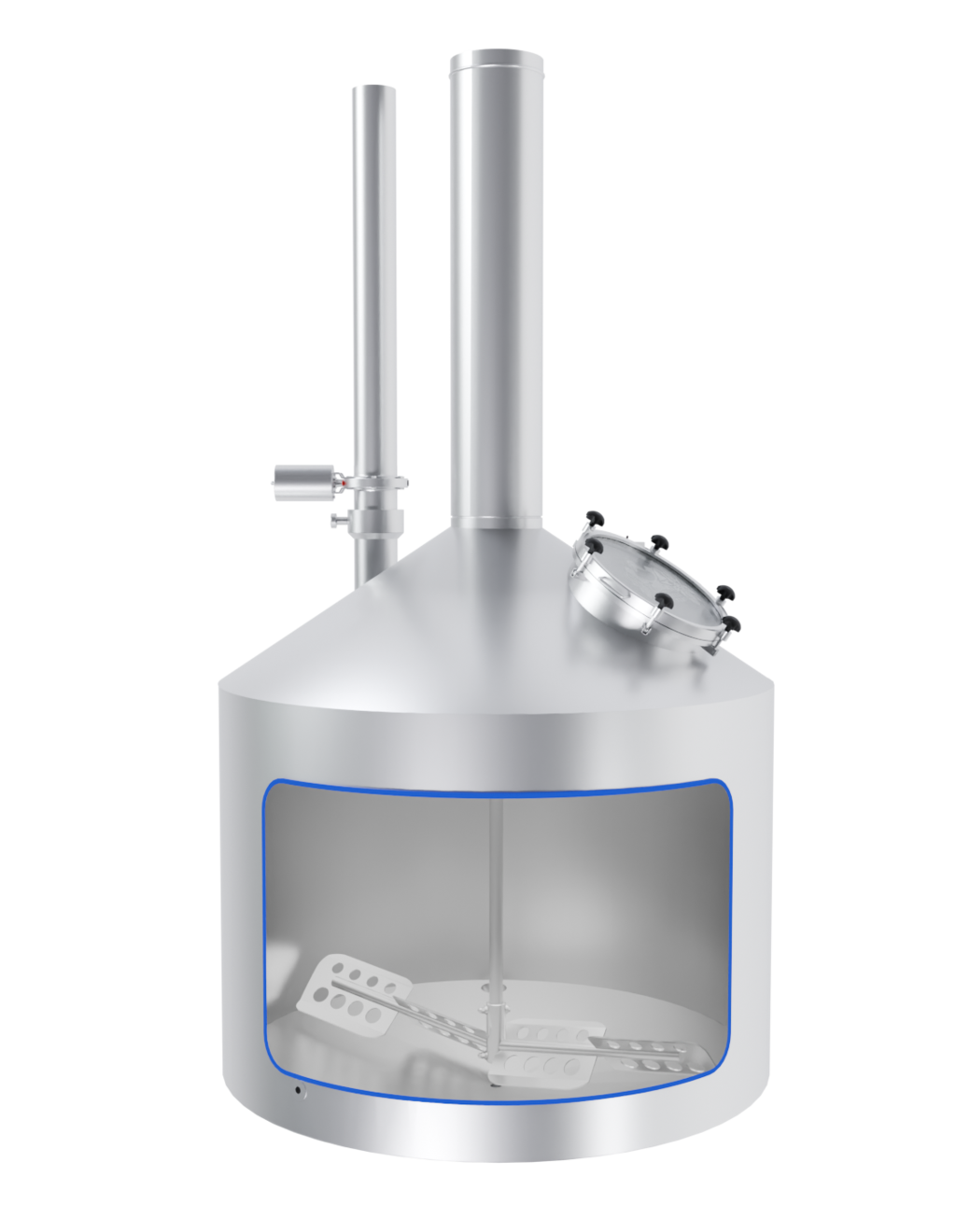
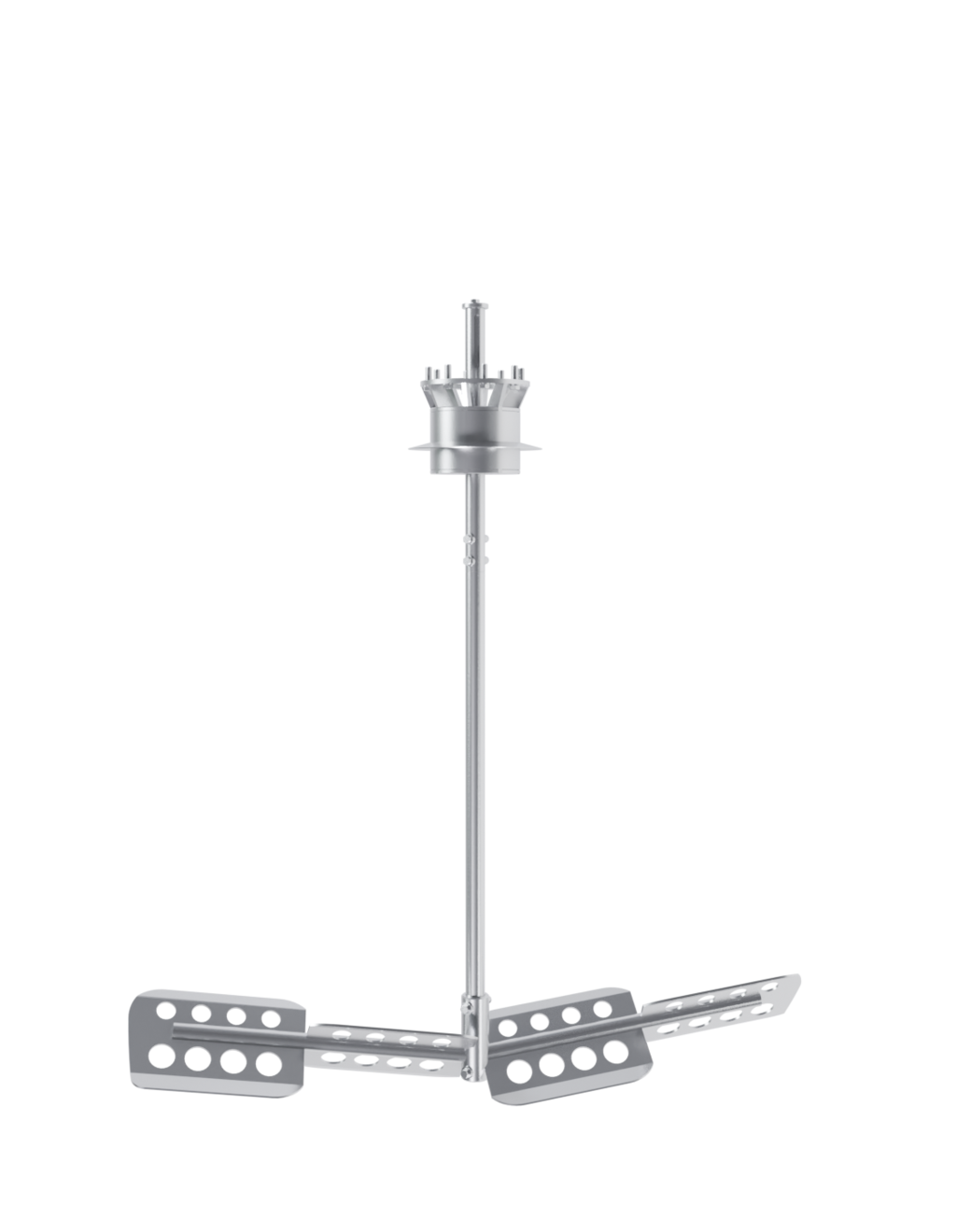
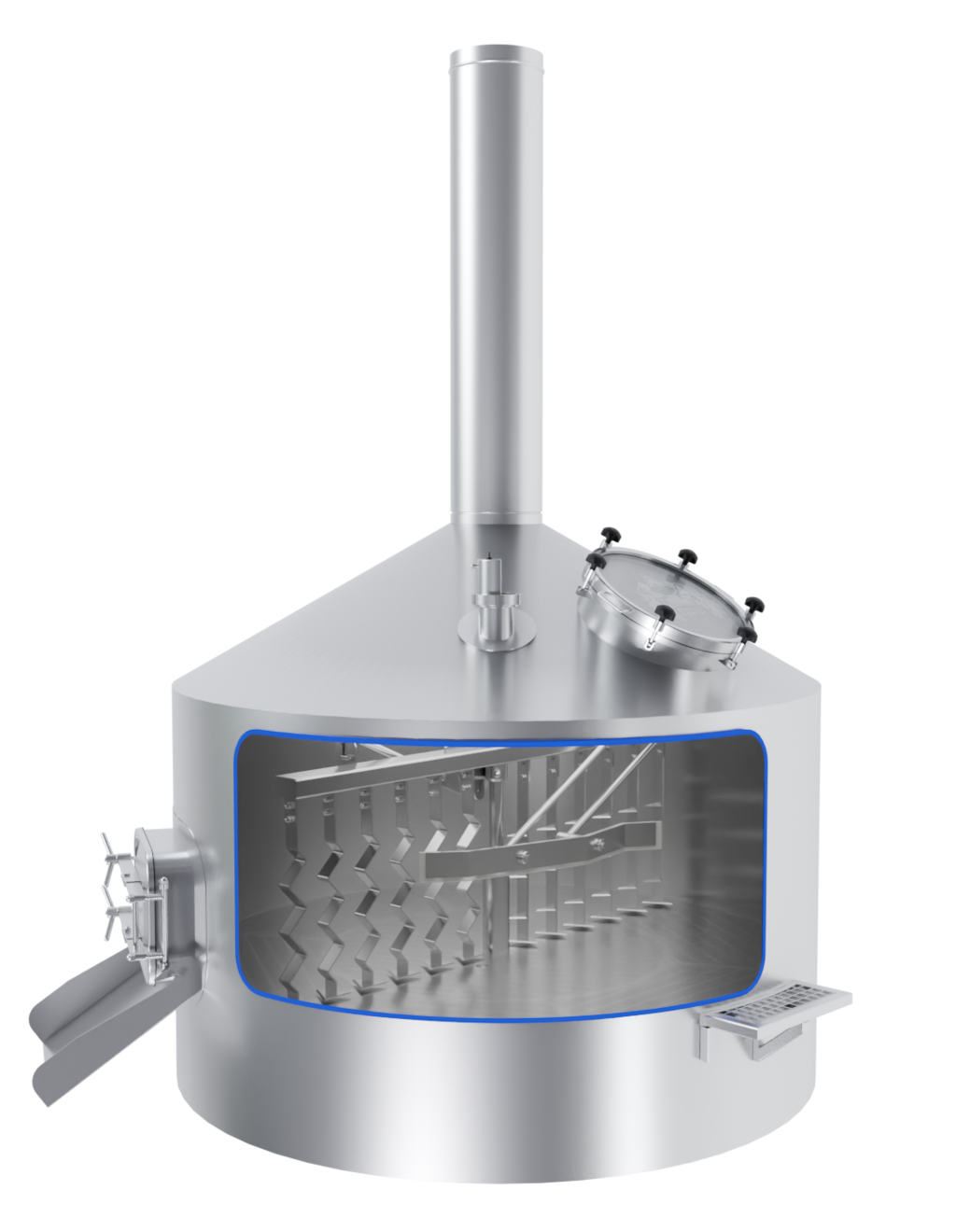
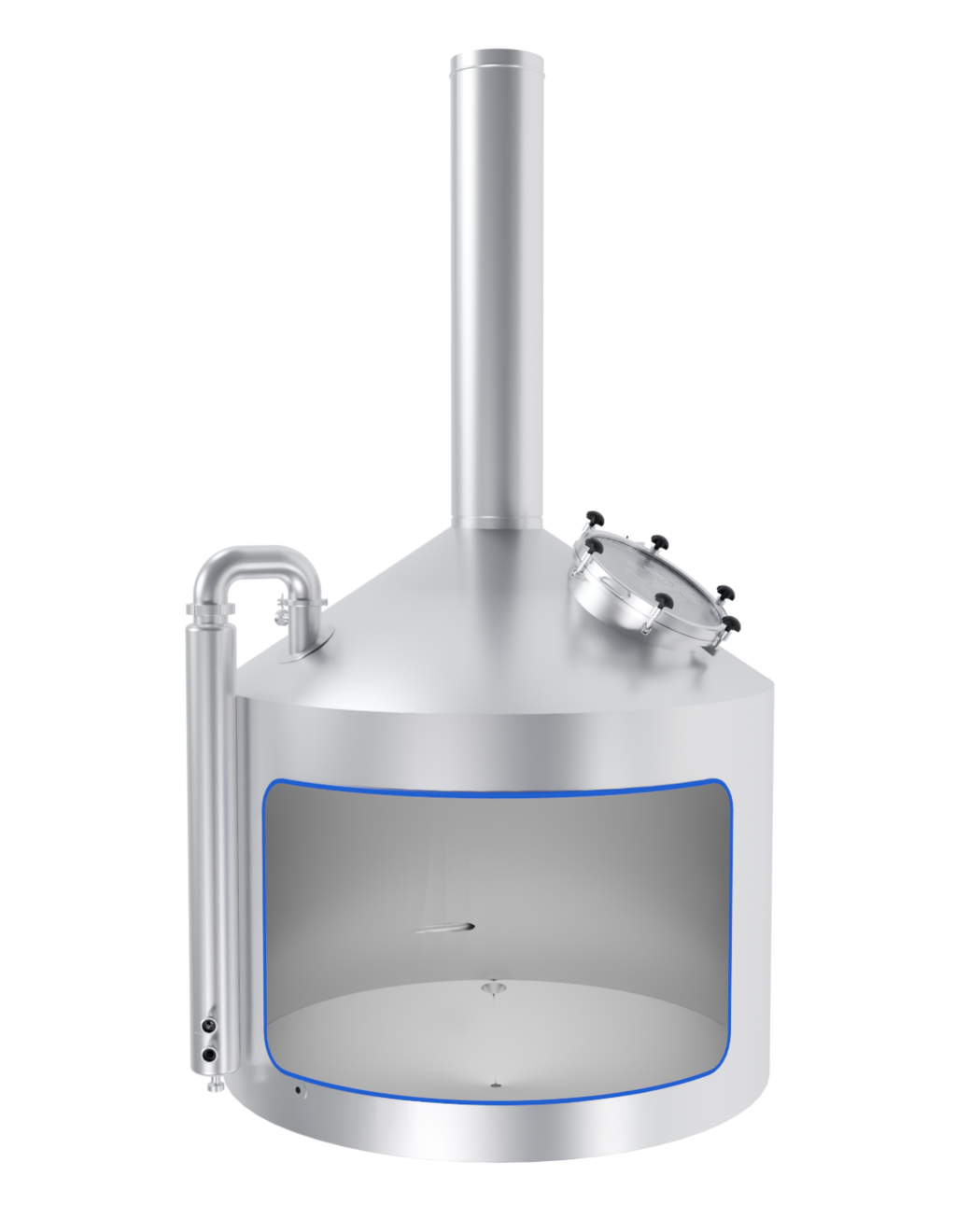
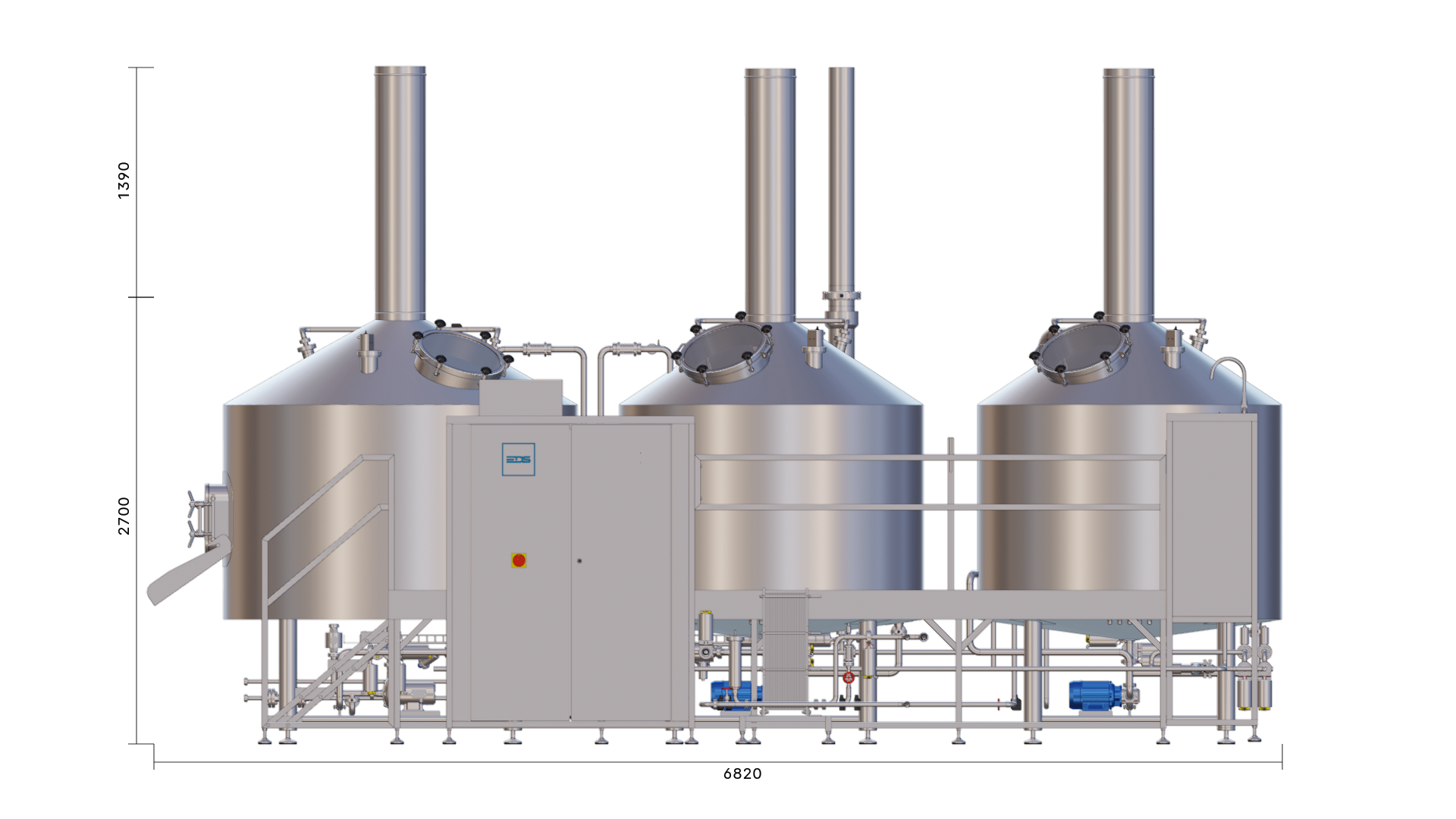
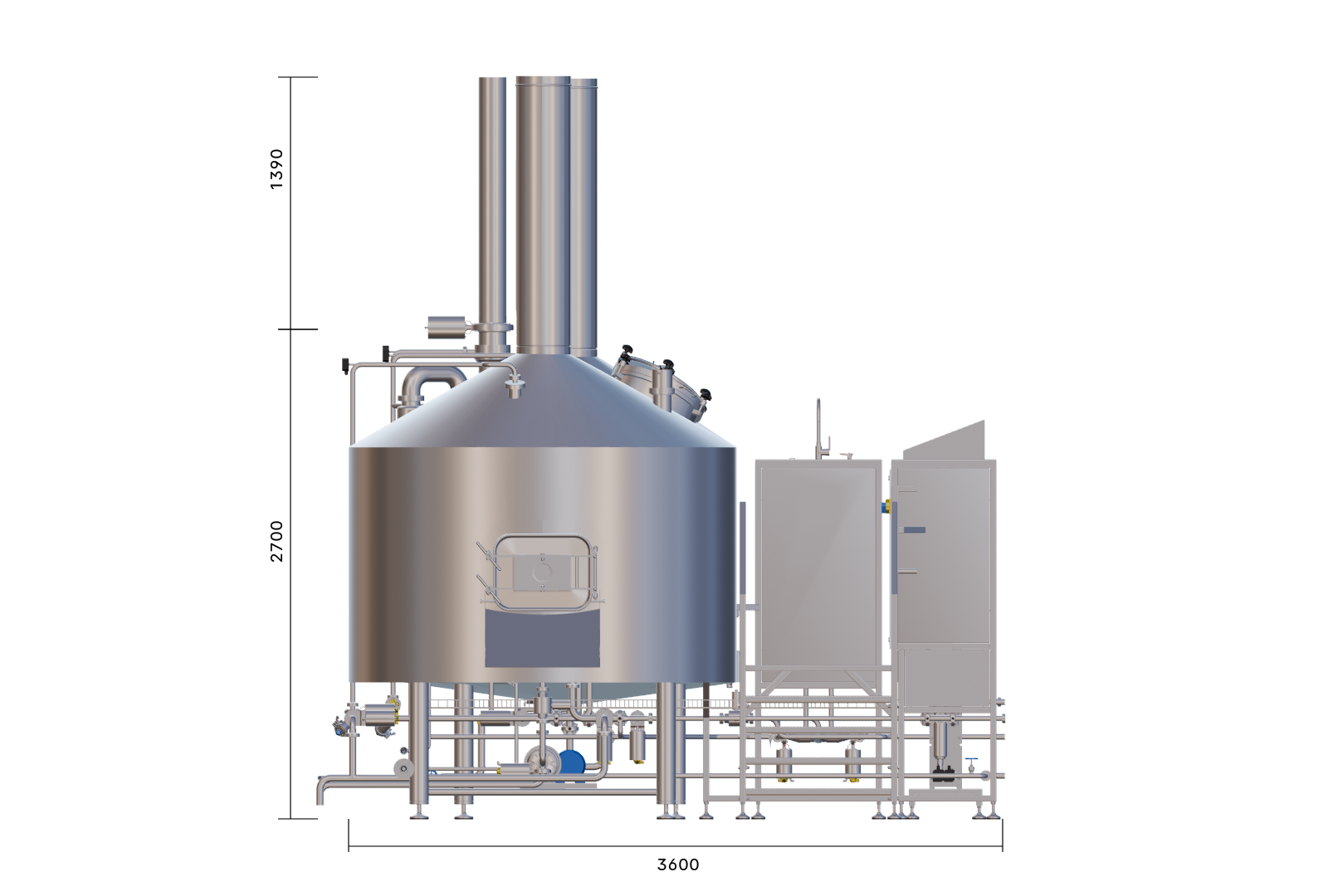
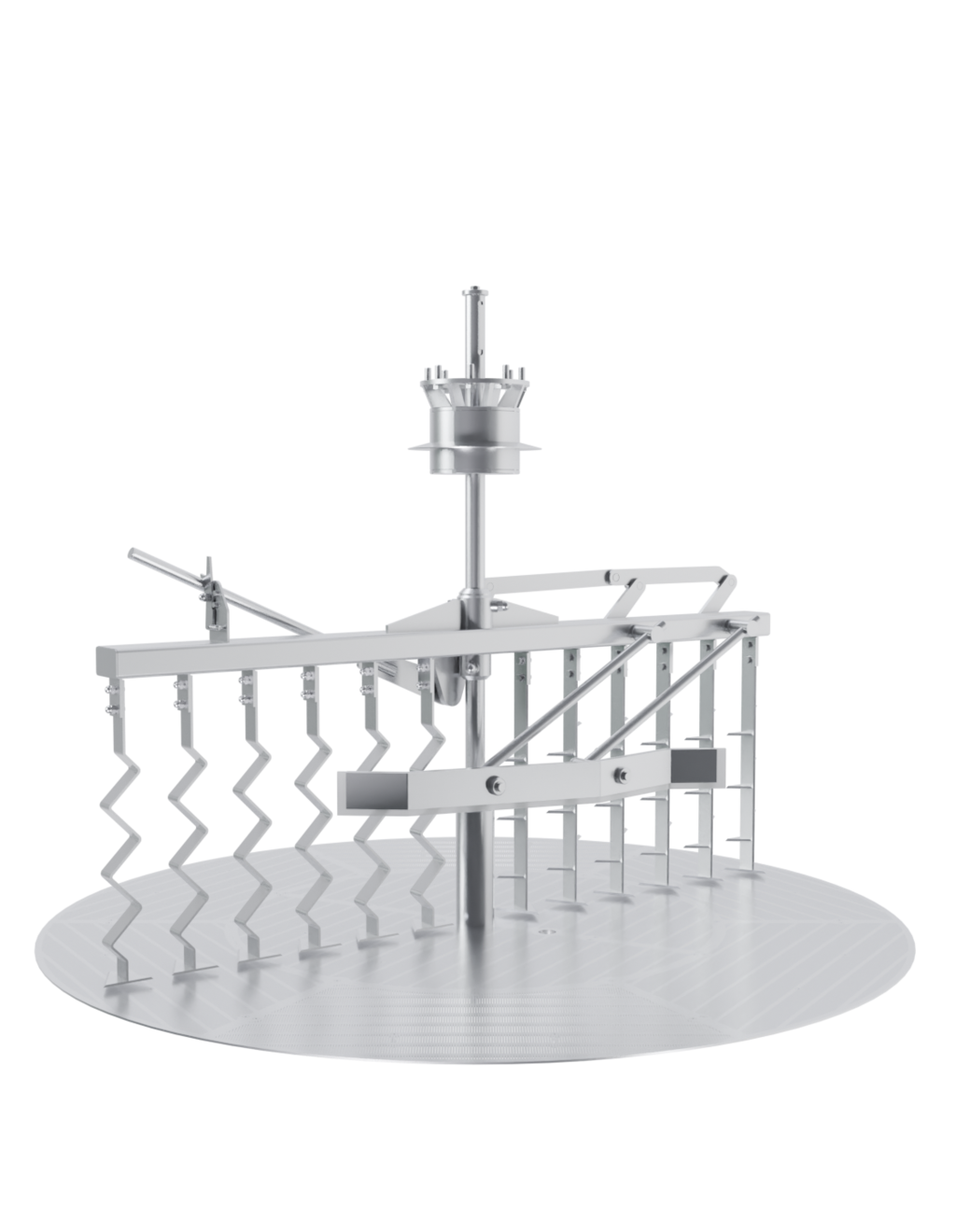
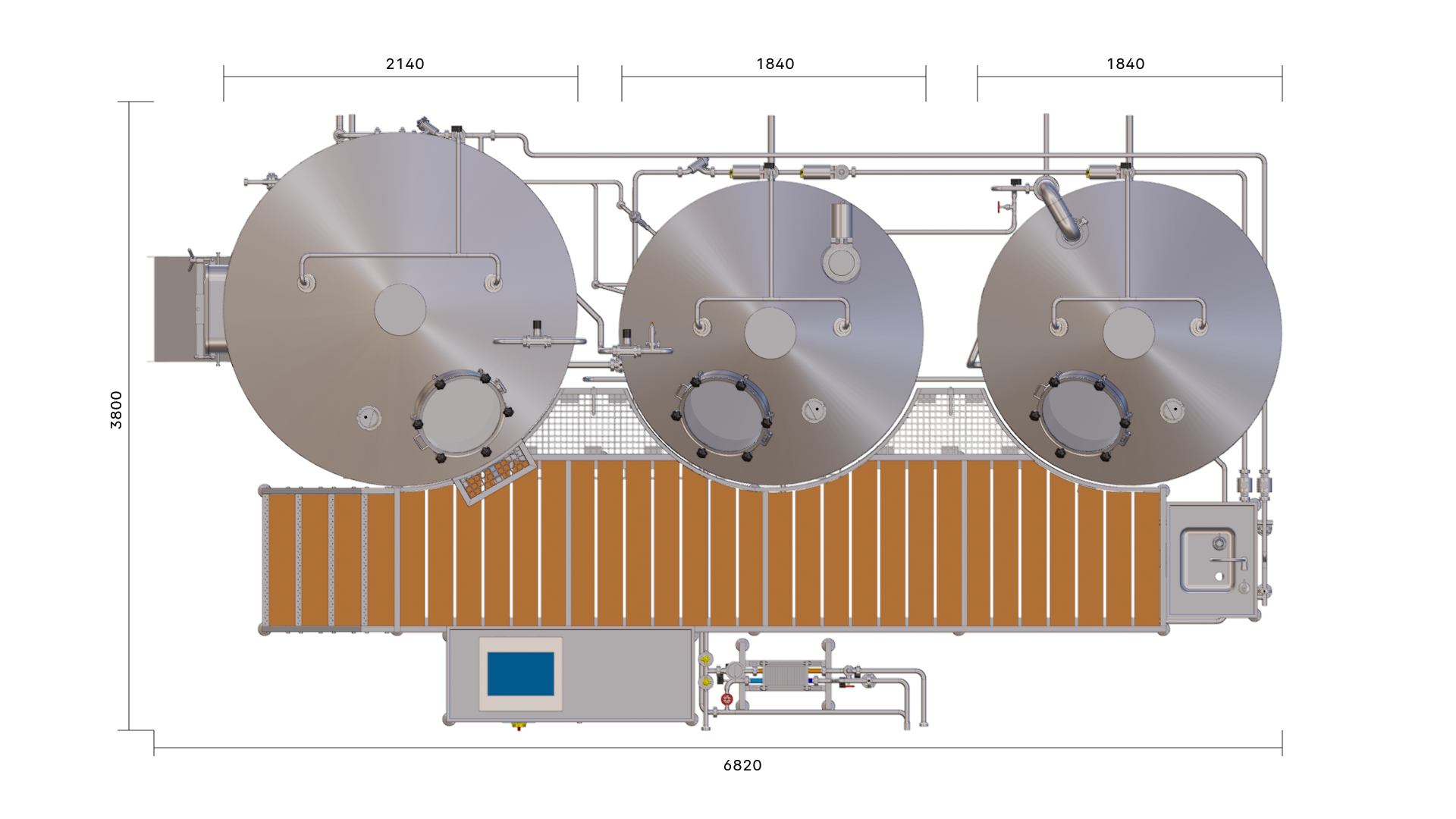
The EDS Grand Craft brewhouse in the three-vessel version consists of three vessels: the mash tun, the lauter tun, and the whirlpool combination. Also included in this variant is the wort cooler. Depending on the brewhouse capacity, up to 6 brews per day are possible in this configuration.
The crushed malt is mashed into the mash tun via the premasher.